Can Shingles Leave Permanent Nerve Damage
Instead the messages become confused and exaggerated causing chronic often excruciating pain that can last months or even years.
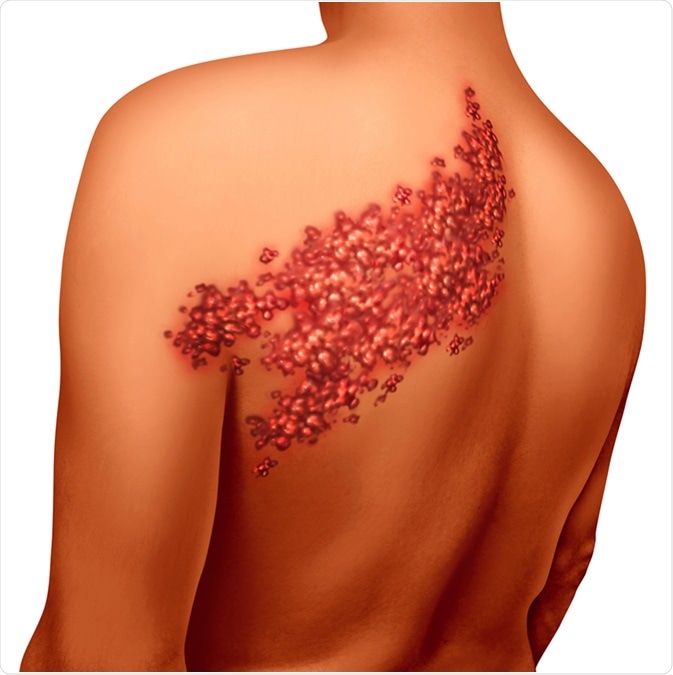
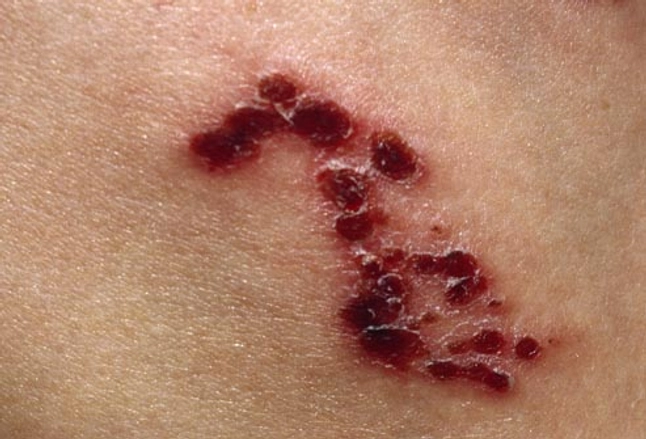
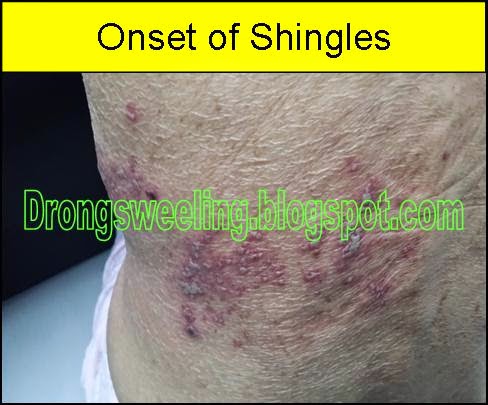
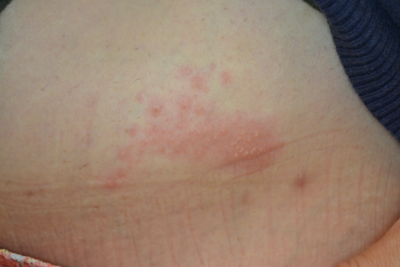
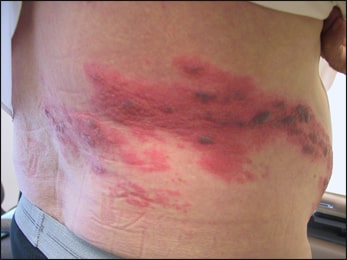
Can shingles leave permanent nerve damage. This can lead to a. Postherpetic neuralgia occurs if your nerve fibers are damaged during an outbreak of shingles. Your symptoms usually go away when the rash is gone. Dealing with a case of shingles is painful enough.
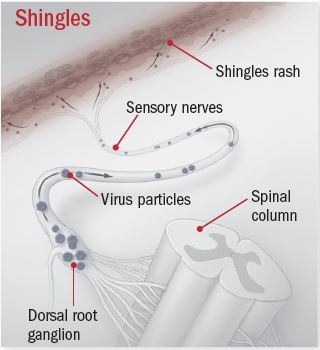
The faulty nerve becomes confused and sends random chaotic pain signals to the brain. This complication is caused by nerve damage called postherpetic neuralgia which is more. Phn occurs when the varicella zoster virus damages the nerves. Damaged fibers can t send messages from your skin to your brain as they normally do.
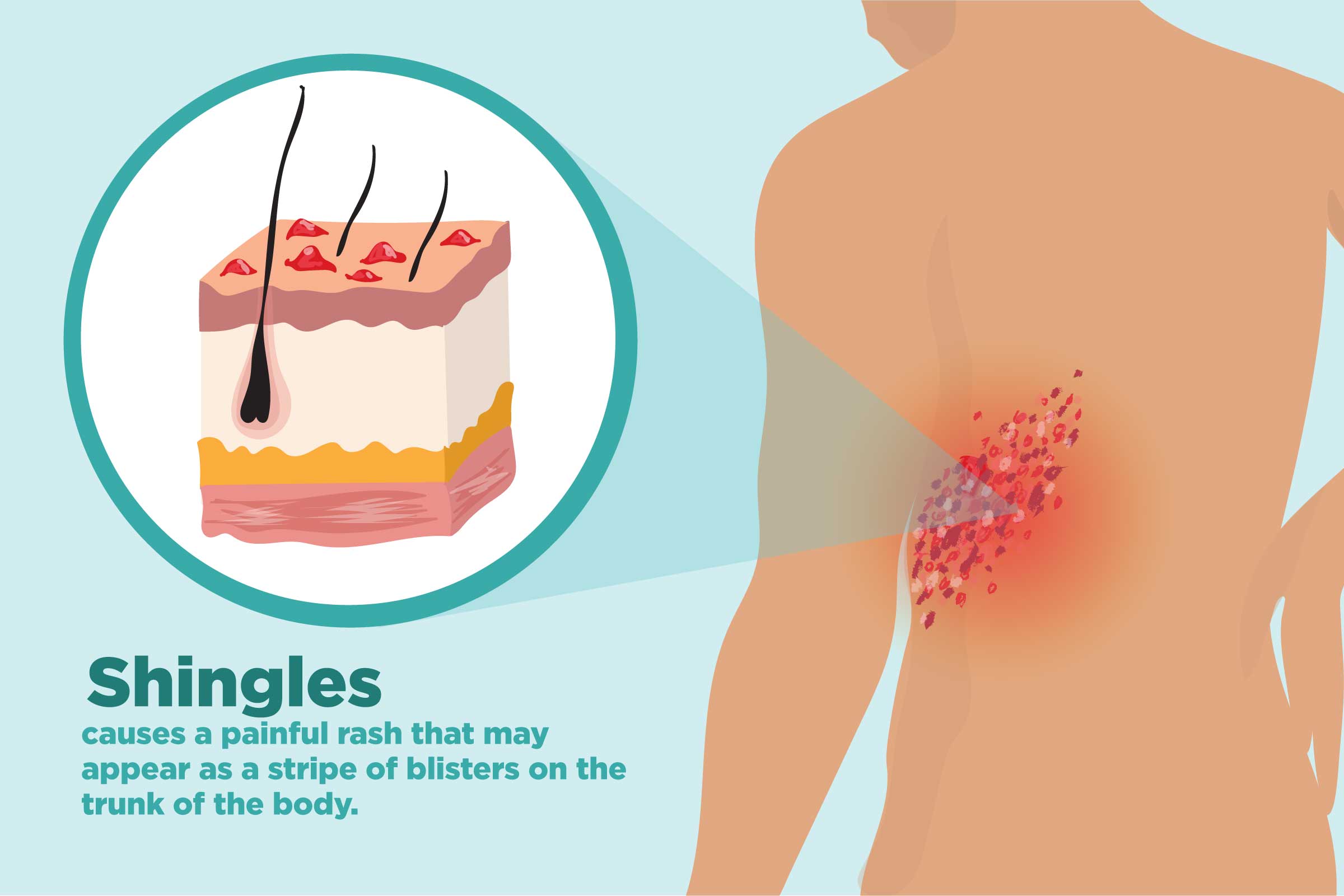
Shingles is caused by the varicella zoster virus the same virus that causes chickenpox. Webmd reports that up to 50 percent of those over age 60 who haven t been treated for their shingles will develop postherpetic neuralgia phn. The nerve damage that is caused by shingles disrupts the proper functioning of the nerve. July 25 2005 a new study offers insights into what helps and what does not help relieve long lasting shingles pain.
The cdc states that approximately 10 to 13 percent of people who get shingles will experience phn. Years later the virus may reactivate as shingles. It s caused by nerve. After you ve had chickenpox the virus lies inactive in nerve tissue near your spinal cord and brain.
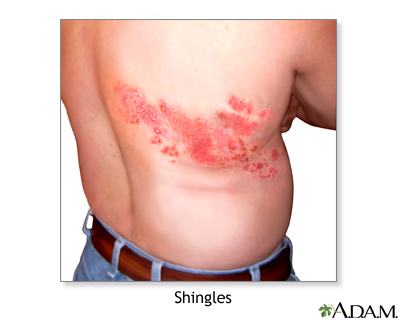
But with phn you may feel pain itching burning and. Doctors call it postherpetic neuralgia or phn. The shingles rash will fade after a few weeks but the pain can continue for many more weeks or months. Postherpetic neuralgia occurs when nerve fibers are damaged permanently by the shingles virus.
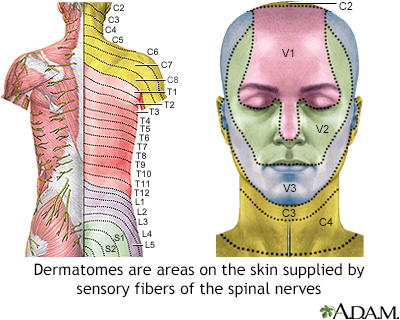
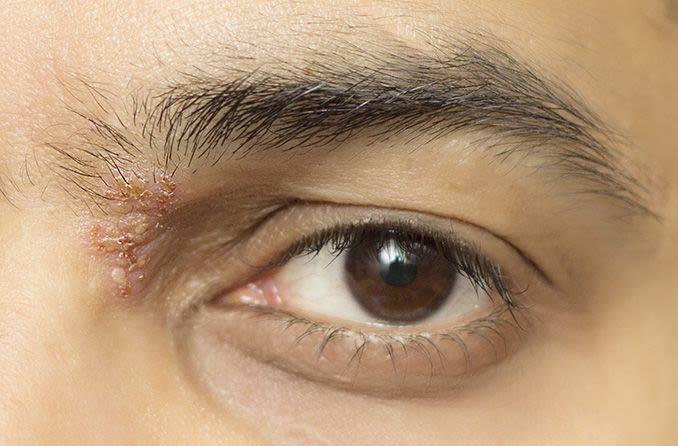
The damaged nerve fibers are unable to properly communicate with the brain sending exaggerated. Postherpetic neuralgia is challenging but help is available. Shingles and facial nerve damage herpes zoster oticus hz oticus is a type of shingles which is restricted to the area in and around the ear and majorly affects the nerves supplying the ear.